How to invest in Starlink? This question sparks intrigue, considering Starlink’s parent company, SpaceX, is a privately held entity, presenting unique challenges and opportunities for investors. This guide delves into the various pathways to potentially participate in SpaceX’s success, exploring both direct and indirect investment strategies. We’ll examine the intricacies of investing in a private company, analyzing Starlink’s market position, and assessing the financial performance and projections of SpaceX.
Crucially, we will also discuss the inherent risks and rewards associated with such ventures.
Understanding the landscape of space-based internet is key. Starlink, with its ambitious constellation of satellites, is revolutionizing global connectivity. This guide aims to provide a clear and comprehensive understanding of the investment options available, allowing you to make informed decisions based on your risk tolerance and financial goals. We will cover everything from direct investment in SpaceX (if and when opportunities arise) to exploring indirect methods via companies benefiting from Starlink’s growth.
Understanding Starlink Investment Options

Investing in Starlink, the satellite internet constellation developed by SpaceX, is not a straightforward process like buying shares of a publicly traded company. Since SpaceX remains a privately held company, direct investment opportunities for the average individual are limited. This section will explore the avenues available and the considerations involved in pursuing such investments.
SpaceX Investment Avenues
Investing in SpaceX, and consequently benefiting indirectly from Starlink’s success, primarily involves participating in private funding rounds. These rounds, typically involving significant capital investments, are not accessible to the general public. Participation usually requires substantial net worth and sophisticated investment experience. Occasionally, secondary market transactions may allow investors to acquire shares from existing investors, but these are rare and often involve complex legal processes.
Another indirect method involves investing in companies that are part of SpaceX’s supply chain or benefit from its technological advancements. However, this approach is highly speculative and requires in-depth research.
Legal and Regulatory Considerations for Investing in SpaceX
Investing in private companies like SpaceX carries unique legal and regulatory implications. These investments are typically subject to less stringent disclosure requirements compared to publicly traded companies. Investors need to understand the terms of the investment agreement, including the valuation, equity stake, and potential risks. Furthermore, legal expertise is often necessary to navigate the complexities of private company investments, especially in regards to securities laws and regulations.
Understanding these complexities and adhering to relevant regulations is crucial to mitigate legal risks.
Risks and Rewards of Investing in Private vs. Public Companies
Investing in a private company like SpaceX presents both higher risks and potentially higher rewards compared to investing in a publicly traded company. The lack of liquidity in private investments means it can be difficult to sell shares quickly, and the valuation is not subject to the daily scrutiny of the public market. However, the potential for significant returns is greater if the company achieves substantial growth, as seen in the case of other successful private companies that eventually went public.
Public companies offer greater liquidity and transparency, but the potential for outsized returns may be more limited.
Participating in Future SpaceX Funding Rounds
Participating in future SpaceX funding rounds is highly unlikely for the average individual. These rounds typically involve institutional investors, venture capitalists, and high-net-worth individuals who can commit substantial capital and meet stringent investment criteria. Access to these rounds often requires established relationships with investment firms or direct connections within SpaceX’s investor network. There’s no publicly available process for individuals to apply for participation in these funding rounds.
Information about future funding rounds is generally not publicly disclosed until after they are completed.
Analyzing Starlink’s Market Position and Potential

Starlink, SpaceX’s satellite internet constellation, occupies a unique position in the rapidly evolving global telecommunications landscape. Its ambitious goal of providing high-speed, low-latency internet access to underserved and remote areas presents both significant opportunities and considerable challenges. Analyzing its market position requires a careful consideration of its competitive advantages, potential growth trajectory, and the factors that could influence its long-term success.Starlink’s competitive advantages stem primarily from its technological innovation and massive scale.
The constellation’s low Earth orbit (LEO) satellites offer significantly lower latency compared to traditional geostationary satellites, resulting in a more responsive and reliable internet experience. Furthermore, Starlink’s sheer number of satellites provides greater coverage and capacity, addressing the limitations of existing satellite internet providers. However, Starlink also faces significant challenges. The high initial cost of equipment and subscription fees can be a barrier to entry for many potential customers, particularly in developing countries.
Competition from other LEO satellite constellations, as well as the ongoing expansion of terrestrial broadband infrastructure, also poses a threat to Starlink’s market dominance.
Starlink’s Competitive Advantages and Disadvantages
Starlink’s competitive advantages include its low latency due to LEO satellites, extensive global coverage enabled by a large constellation, and the potential for high bandwidth capabilities. Conversely, disadvantages include high upfront costs for user terminals, ongoing subscription fees which may be unaffordable for some, and the potential for interference from other satellite constellations or terrestrial networks. The company’s reliance on a complex and expensive satellite network also presents a vulnerability.
For example, the need for frequent satellite launches and maintenance represents a significant ongoing expense. Furthermore, regulatory hurdles and potential space debris issues pose operational challenges.
Global Satellite Internet Market Growth and Starlink’s Projected Market Share
The global satellite internet market is experiencing substantial growth, driven by increasing demand for broadband access in underserved regions and the limitations of terrestrial infrastructure in remote areas. Analysts predict significant expansion in the coming years, with various market research firms offering varying projections. For instance, a report by [insert reputable market research firm and report name here] projected a market size of [insert projected market size] by [insert year].
While precise market share predictions for Starlink are difficult due to the dynamic nature of the market and the emergence of competitors, Starlink aims to capture a significant portion of this growth, leveraging its technological advantages and aggressive expansion strategy. Their success will depend heavily on their ability to manage costs, overcome regulatory hurdles, and maintain technological leadership.
Key Factors Influencing Starlink’s Future Success or Failure
Several key factors will determine Starlink’s future success or failure. These include technological advancements in satellite technology and network management, the effectiveness of their customer acquisition strategies, and the ability to maintain a competitive pricing structure. Government regulations concerning spectrum allocation and satellite operations will also play a crucial role. Furthermore, successful mitigation of space debris and the maintenance of a reliable and resilient satellite constellation are essential for long-term sustainability.
The level of competition from other satellite internet providers and terrestrial broadband networks will also significantly impact Starlink’s market share and profitability. For example, the success of other LEO constellations like OneWeb could directly impact Starlink’s market penetration.
Starlink SWOT Analysis
Starlink’s strengths include its technological innovation (low latency, high bandwidth), extensive global coverage, and strong brand recognition associated with SpaceX. Weaknesses include high initial costs for users, ongoing subscription fees, and reliance on a complex and expensive satellite network. Opportunities include the expansion into underserved markets, partnerships with telecommunications companies, and the potential for integration with other SpaceX technologies.
Threats include competition from other satellite internet constellations, advancements in terrestrial broadband technology, and potential regulatory challenges. A successful strategy will require Starlink to leverage its strengths, mitigate its weaknesses, capitalize on opportunities, and effectively address the threats to maintain its competitive advantage.
Assessing the Financial Performance and Projections of SpaceX
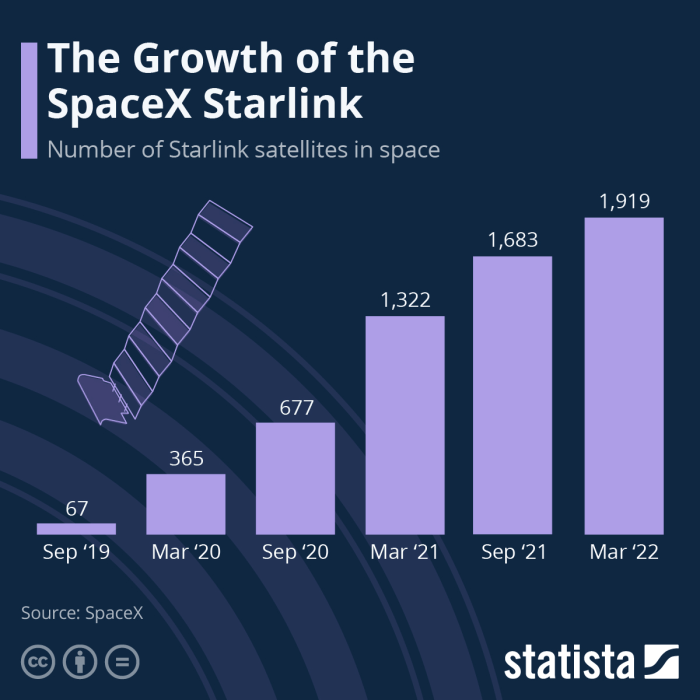
SpaceX, while a privately held company, is a significant player in the aerospace industry, and understanding its financial health is crucial for assessing the potential of Starlink, its satellite internet constellation. However, due to SpaceX’s private status, comprehensive financial data is limited. We will examine the publicly available information and draw inferences where possible.
SpaceX’s Publicly Available Financial Data
Precise revenue, expense, and profitability figures for SpaceX remain undisclosed. The company occasionally releases limited information, often focusing on achievements rather than detailed financial statements. News reports and industry analyses provide estimates, but these should be treated with caution due to their reliance on incomplete data and varying methodologies. For instance, reports suggest SpaceX’s revenue has grown substantially year-over-year, driven primarily by Starlink subscriptions and launch contracts.
However, the precise revenue figures and profit margins remain largely unknown. Similarly, information regarding operational expenses, including research and development costs, is scarce. This lack of transparency makes a precise assessment of SpaceX’s financial performance challenging.
Comparison of SpaceX’s Financial Performance with Competitors
Given the limited public financial data for SpaceX, a direct comparison with publicly traded competitors like Boeing or Lockheed Martin requires significant qualification. The following table presents a comparative analysis based on available, albeit limited, information and estimations from reputable industry sources. The absence of key metrics for SpaceX highlights the challenge in making a precise comparison.
| Metric | SpaceX (Estimates) | Boeing | Lockheed Martin |
|---|---|---|---|
| Annual Revenue (USD Billion) | ~10 (Estimate, varies across sources) | ~66 (2022) | ~66 (2022) |
| Revenue Growth (Year-over-Year %) | High (Estimates vary widely) | ~3% (2022) | ~3% (2022) |
| Market Capitalization (USD Billion) | N/A (Private Company) | ~150 (2023) | ~110 (2023) |
| Profit Margin (%) | Unknown | ~10% (2022) | ~10% (2022) |
*Note: Figures for Boeing and Lockheed Martin are based on their publicly released financial reports for 2022 and are subject to change.*
Analysis of SpaceX’s Financial Projections and Future Growth Potential
Projecting SpaceX’s future financial performance involves significant uncertainty. The success of Starlink, coupled with the increasing demand for space-based services, suggests strong growth potential. However, challenges remain, including intense competition, regulatory hurdles, and the substantial capital investment required for further expansion. Analysts offer a range of projections, often emphasizing the potential for exponential growth if Starlink achieves its market penetration targets and SpaceX secures additional launch contracts.
Successful development and deployment of Starship could significantly impact SpaceX’s revenue streams and profitability. However, the timing and success of this project remain significant unknowns.
Impact of Government Regulations and Funding on SpaceX’s Financial Performance
Government regulations, both in the US and internationally, significantly influence SpaceX’s operations and financial performance. Regulatory approvals for launches, spectrum allocation for Starlink, and export controls on technology all impact costs and timelines. Government funding, either directly through contracts or indirectly through supportive policies, can play a crucial role in SpaceX’s growth trajectory. For example, NASA contracts contribute significantly to SpaceX’s revenue, while supportive regulatory frameworks facilitate Starlink’s expansion.
Conversely, restrictive regulations or a lack of government support could hinder SpaceX’s growth and profitability.
Exploring Indirect Investment Methods

Investing directly in SpaceX, the parent company of Starlink, is currently not feasible for most individual investors. However, the significant growth potential of Starlink presents opportunities for indirect investment through companies that benefit from its success. This approach allows participation in the Starlink ecosystem without the limitations of direct SpaceX investment. This section explores these alternative investment avenues.
Companies Benefiting from Starlink’s Infrastructure, How to invest in starlink
Starlink’s global satellite internet network requires extensive ground infrastructure, including ground stations, data centers, and fiber optic networks. Companies involved in building and maintaining this infrastructure are poised to benefit significantly from Starlink’s expansion. These companies may include established telecommunications providers, fiber optic cable manufacturers, and data center operators who provide crucial support services. For example, a company specializing in the construction of ground stations for satellite communication could see increased revenue as Starlink continues its global rollout.
The financial performance of such a company would likely be positively correlated with Starlink’s growth and market penetration.
Companies in the Starlink Supply Chain
Starlink’s operations involve a complex supply chain encompassing satellite manufacturing, launch services, and ground equipment. Identifying companies involved in these aspects offers another route for indirect investment. For instance, companies manufacturing components for Starlink’s satellites, providing launch services (although this is largely dominated by SpaceX itself), or supplying specialized ground equipment could experience substantial growth aligned with Starlink’s success.
However, pinpointing specific companies involved is challenging due to SpaceX’s relatively opaque supply chain. Publicly available information regarding specific suppliers is limited, often for reasons of commercial confidentiality.
Risk and Return Comparison: Indirect vs. Direct Investment
Investing in companies indirectly connected to Starlink presents a different risk profile compared to a hypothetical direct investment in SpaceX (were it possible). Direct investment, if available, would offer potentially higher returns but also carry significantly higher risk. SpaceX, as a private company, has limited transparency and its stock performance is not subject to the same regulatory scrutiny as publicly traded companies.
Indirect investment, on the other hand, offers diversification and reduced risk, as the performance of the chosen company is not solely dependent on Starlink’s success. However, the potential returns are likely to be lower than a direct investment in SpaceX if that were possible. The overall risk and return profile should be carefully considered within the context of an investor’s overall portfolio strategy.
Potential Indirect Investment Avenues
The following list presents potential avenues for indirect investment in the Starlink ecosystem, outlining their associated advantages and disadvantages. It is important to conduct thorough due diligence before making any investment decisions.
- Telecommunications Infrastructure Companies: Pros: Relatively stable businesses with established revenue streams. Cons: Limited direct exposure to Starlink’s high-growth potential; performance may be influenced by broader market trends.
- Fiber Optic Cable Manufacturers: Pros: Direct benefit from Starlink’s need for extensive fiber optic networks. Cons: Subject to commodity price fluctuations and competition within the fiber optic industry.
- Data Center Operators: Pros: Increased demand for data center capacity due to Starlink’s data processing needs. Cons: High capital expenditure requirements for data center construction and maintenance.
- Aerospace Component Manufacturers (if identifiable): Pros: Direct exposure to Starlink’s satellite manufacturing. Cons: Difficult to identify specific companies involved; high reliance on a single customer (SpaceX).
Understanding the Risks Involved: How To Invest In Starlink

Investing in SpaceX, and consequently Starlink, presents significant opportunities for substantial returns, but it’s crucial to acknowledge the inherent risks associated with such a venture. SpaceX operates in a high-growth, high-risk sector characterized by volatile market conditions and unpredictable technological challenges. A thorough understanding of these risks is paramount before committing any capital.
Inherent Risks of Investing in High-Growth Companies
High-growth companies, by their very nature, are often characterized by higher levels of risk compared to established, mature businesses. SpaceX, as a pioneer in space exploration and commercial satellite internet, faces numerous challenges. These include the inherent uncertainties of technological development, the competitive landscape, and the complexities of regulatory environments. A failure to meet ambitious technological milestones, for instance, could severely impact the company’s valuation and investor returns.
Similarly, intense competition from established players or new entrants could erode market share and profitability. Furthermore, government regulations and licensing requirements in the aerospace industry can be complex and unpredictable, potentially delaying projects or increasing costs. These factors contribute to the inherent volatility associated with investing in such a company.
Technological Disruptions and Unforeseen Events
The success of Starlink hinges on continuous technological advancements and operational reliability. Technological disruptions, either from internal setbacks or external innovations, could significantly impact Starlink’s business model. For example, the emergence of a superior satellite internet technology or a significant improvement in terrestrial broadband infrastructure could reduce the demand for Starlink’s services. Similarly, unforeseen events, such as major satellite failures, cyberattacks, or geopolitical instability in regions served by Starlink, could disrupt operations and negatively impact profitability.
The reliance on a complex, interconnected network of satellites also increases the potential for cascading failures, which could have significant financial consequences. Considering the long-term nature of space-based infrastructure projects, these risks must be carefully weighed against potential returns.
Importance of Portfolio Diversification
Given the inherent risks associated with investing in SpaceX or Starlink, diversification is crucial for any investor. Diversification involves spreading investments across a range of asset classes, sectors, and geographies to reduce the overall risk of a portfolio. By diversifying, investors can mitigate the potential impact of a negative event affecting a single investment. For instance, if SpaceX faces significant setbacks, a diversified portfolio containing investments in other sectors (e.g., technology, healthcare, real estate) can help cushion the blow and prevent significant overall losses.
The optimal level of diversification will depend on individual risk tolerance and investment goals, but it’s generally recommended to avoid over-concentrating investments in a single, high-risk asset.
Risk-Reward Profile of SpaceX Investment
A visual representation of SpaceX’s risk-reward profile could be depicted as a graph. The X-axis would represent the potential return on investment, ranging from significant losses to substantial gains. The Y-axis would represent the probability of achieving those returns. The graph would show a skewed distribution, with a long tail extending towards significant gains, reflecting the potential for high rewards.
However, a significant portion of the distribution would also lie in the negative return region, highlighting the considerable risk of substantial losses. This visualization would clearly demonstrate that while the potential for high returns is present, the probability of losses is also significant, especially in the short term. For example, a scenario with a 10% probability of a 1000% return, but a 30% probability of a 50% loss, would be illustrative of this high-risk, high-reward profile, typical of investments in early-stage, high-growth companies.
Closing Summary

Investing in Starlink, or more accurately, in its parent company SpaceX, presents a compelling yet complex opportunity. While the potential rewards are significant, given Starlink’s disruptive technology and the burgeoning satellite internet market, the inherent risks associated with investing in a private, high-growth company must be carefully considered. This guide has provided a framework for understanding the various avenues for participation, from direct investment (when possible) to indirect approaches through related businesses.
Ultimately, a thorough due diligence process, a clear understanding of your risk tolerance, and diversification within your investment portfolio are paramount to making informed decisions in this exciting, yet volatile, sector.